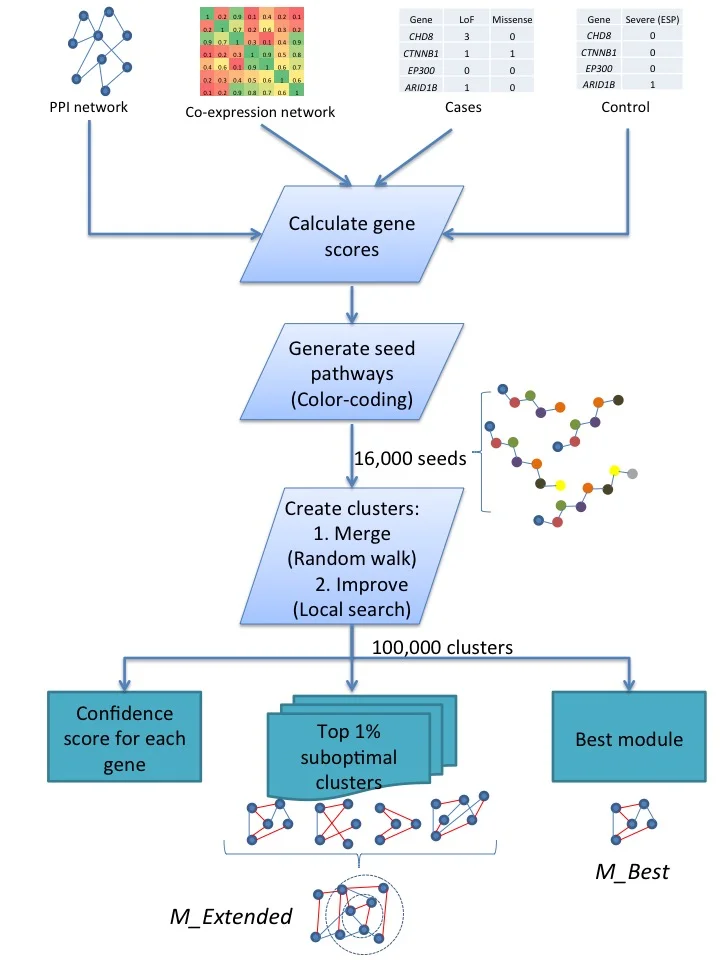
One of the main themes of research in the lab is to develop combinatorial algorithms and machine learning methods to utilize various types of biological data to better understand complex disorders with a special focus on neurodevelopmental disorders (e.g. autism). As more genomes and exomes of cases are being sequenced, we will continue to discover additional variants. However, it is difficult to understand if these variants do in fact cause the disorder, and if so, what is their precise functional consequence. One of the fundamental hypothesis being studied in our lab is that a significant fraction of causative variants in a complex disorder disrupt a small number of pathways or complexes. We have previously developed a novel method for disease module discovery called MAGI [1]. MAGI combines information from both protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks and gene expression profiles during brain development to find modules of genes enriched in de novo mutations in probands with neurodevelopmental disorders (Figure 1). The method identifies sets of genes that are densely connected while maximizing the number of de novo mutations covered in probands.
We are actively developing novel combinatorial algorithms to predict more coherent set of gene modules and pathways that are disrupted in complex disorders. Furthermore, we are also developing machine learning methods to utilize the modules found to predict novel disease genes.
[1] Hormozdiari F, Penn O, Borenstein E, Eichler EE. The discovery of integrated gene networks for autism and related disorders. Genome Research 2015 Jan; 25(1) 142-54 do:10.1101/gr178855.114 Epub 2014 Nov 5
Figure 1. MAGI method for genetic module discovery.